Elastomers
General information about elastomers

|
Elastomers are special polymers known for their exceptional elasticity and ability to return to their original shape after deformation. (Typically: to recover within 10% of their original length after being stretched 100% for five minutes.) |
|
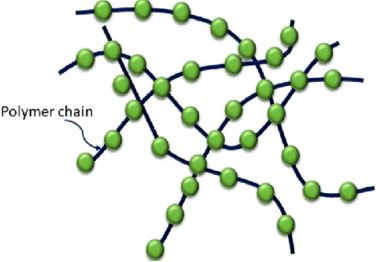
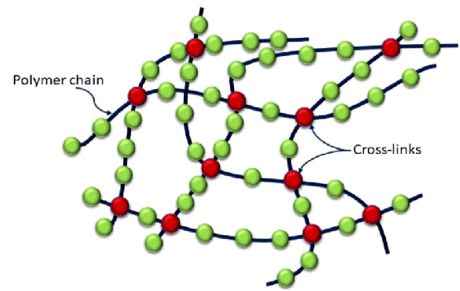
| The chemical structure of elastomers fundamentally differs from that of conventional plastics. The most significant distinction among polymers is the presence of numerous cross-linkages between polymer chains in elastomers. These cross-linkages are responsible for the distinctive elasticity and resilience of elastomers.
|
|
|
Elastomers are commonly referred to as either natural or synthetic rubber. Natural rubber comes from latex, produced by some trees. Today, numerous synthetic elastomers exist, including neoprene, silicone rubber, and fluorosilicone rubber, each tailored for specific applications due to their unique properties. |
|
The most prevalent application of elastomers is in rubber manufacturing. Through a process called vulcanization, heat is applied to create cross-linkages in rubber.
The components of rubber compounds can vary depending on the specific application and desired properties. However, in general, rubber compounds typically consist of the following main components:
Rubber Base: The foundation of rubber compounds is formed by the rubber material or elastomer. These can be synthetic or natural rubbers, such as natural rubber, neoprene rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), polyurethane, or silicone. The chosen rubber base determines the material's elasticity, resistance, and other key properties.
Additives: These materials are added to the rubber compound to enhance or modify its properties. Examples of additives include:
Fillers: Such as carbon black or silica, which increase the stiffness and abrasion resistance of the rubber compound.
Vulcanizing Agents: These substances aid in the formation of cross-links in the rubber compound, such as sulfur or peroxides.
Reinforcing Agents: Compounds like resins or cotton fibers that strengthen the rubber.
Plasticizers: Materials like sodium oils or paraffins that increase flexibility and reduce rigidity.
Colorants: Compounds that give the rubber compound its desired color.
Antioxidants: Substances that prevent aging and degradation of the rubber compound.
Performance Enhancers: These compounds are added to the rubber compound to impart specific properties. For instance:
UV Stabilizers: Protect the rubber compound from damage caused by UV radiation.
Heat and Cold Resistant Additives: Help improve the compound's resistance to extreme temperatures.
The measurable characteristics of elastomers include the following:
Elasticity/Flexibility: The primary characteristic of elastomers is their elasticity, which is the ability of the material to deform in response to force and return to its original shape. This property indicates how much an elastomer can stretch or compress and then recover its initial form.
Temperature Range: Elastomers can operate effectively within specific temperature ranges. Measurable characteristics include the temperature range in which the material retains its elasticity and functional properties. For example, some elastomers may stiffen or crack at low temperatures.

Hardness: Hardness of elastomers can be measured on a scale, such as the Shore hardness scale. Hardness indicates how resistant the material is to indentation or scratching and how pliable or rigid its surface is.
Wear Resistance/Abrasion resistence: Wear resistance is crucial in applications where elastomers come into continuous contact with other surfaces. Measuring wear resistance can be done using various methods, such as measuring material loss or the extent of wear marks.

Tensile Strength: Tensile strength of elastomers reveals how much stress the material can withstand before it undergoes rupture. The measurement of tensile strength generally indicates the material's load-bearing capacity.
Elongation: Elongation measures how much an elastomer can stretch compared to its original length. This property is important in applications like rubber products, where flexibility and elongation are critical.
Recovery: Recovery capability shows how well an elastomer can return to its original shape after deformation. Recovery indicates the material's durability and long-term performance.
Dielectric Properties: Dielectric properties of elastomers determine their electrical insulating capacity and resistance to electrical current flow.
Chemical Resistance: The reaction of elastomers to various chemical substances can be measured. This information is important when using the material in chemical environments.
UV Stability: UV stability indicates how well elastomers resist premature aging and damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Compression set resistance: The percentage of the original specimen thickness after axially directed pushing forces are applied and released over a set temperature and time (ASTM D395).
Adhesion: Ability of the material to cling to the metallic case (ASTM D429).
Modulus: is the stress required to produce a given force.

Tear resistance: Is the capacity of a material to resist the growth of a cut when tension is applied (ASTM D624).
Resilience: The ability to absorb temporary energy without creating a permanent distortion (ASTM D945).

KTT Sealing Technologies is currently the only manufacturer of sealing elements in Hungary that offers a wide range of sizes for all types of oil seals made of all widely used elastomer materials.
Our main activities are the production of oil seals as well as, the wholesale and retail sale of oil seals, O-rings, hydraulic seals, mechanical and technical assembly goods.
Contacts
KTT Kubinszky Sealing Technologies Ltd.9400 HUNGARY, Sopron, Besenyő str. 24/B.
Local Tax number: 11462390-2-08
EC VAT Number: HU11462390
Phone: +36 99 / click
E-mail: click
Monday–Friday: 9.00–16.00
Inventory information
The stock information on the webshop is real and constantly updated. We regularly expand our range based on customer demand.
If you are looking for special rubber products, contact us – KTT is your professional partner in sealing technology.

The KTT Kubinszky Sealing Technologies Ltd
is part of the Axel Johnson International Group.
Our references
BorgWarner, Bosch, Festo, Grundfos, Caterpillar, KUKA Robotics, Electrolux